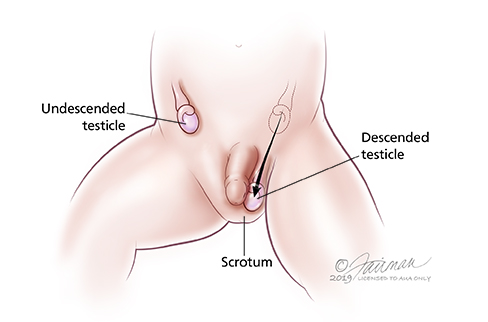
 Cryptorchidism: Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment - Urology Care Foundation
Cryptorchidism: Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment - Urology Care FoundationDo not delay your attention at Mayo ClinicRemarked Conditions Diagnosis If your child has an unwanted testicle, your doctor may recommend surgery for diagnosis and potential treatment: Laparoscopic. A small tube containing a camera is inserted through a small incision in your child's abdomen. Laparoscopy is done to locate an intraabdominal testicle. The doctor may be able to fix the unwanted testicle during the same procedure, but additional surgery may be needed in some cases. Alternatively, laparoscopy may show any present testicle, or a small remnant of non-functional testicular tissue that is removed. After birth, if the doctor cannot detect any testicles in the scrotum, he could order more tests to determine if the testicles are not there at all instead of not neglected. Some conditions that result in absent testicles may cause serious medical problems shortly after birth if not diagnosed and not treated. Image tests, such as ultrasound and magnetic resonance, are usually not recommended to diagnose an unwanted testicle. Care at the Mayo Clinic Learn More Treatment The aim of the treatment is to move the unwanted testicle to its proper location in the scrotum. Treatment before 1 year of age could reduce the risk of complications of an unwanted testicle, such as infertility and testicular cancer. Before it is better, but it is recommended that surgery take place before the child is 18 months old. SurgeryAn unwanted testicle is usually corrected with surgery. The surgeon carefully manipulates the testicle in the scrotum and sutures it instead (orchiopexia). This procedure can be done with a laparoscope or open surgery. When your child has surgery, it will depend on several factors, such as your health and the difficulty of the procedure. Your surgeon is likely to recommend surgery when your child is about 6 months old and before he or she is 12 months old. Early surgical treatment seems to decrease the risk of subsequent complications. In some cases, the testicle could be undeveloped, abnormal or dead tissue. The surgeon will remove this testicular tissue. If your child also has an inguinal hernia associated with the unwanted testicle, hernia is repaired during surgery. After surgery, the surgeon will supervise the testicle to see that it continues to develop, works properly and stays in place. Surveillance may include: Hormone Treatment Hormone therapy involves injection of human choraline gonadotropin (HCG). This hormone could cause the testicle to move to your child's scrotum. Hormonal treatment is not usually recommended because it is much less effective than surgery. Other treatments If your child does not have one or both testicles—because either one or both are missing or not survived after surgery—you may consider testicular saline prosthesis for the scrotum that can be implanted during late childhood or adolescence. These prostheses give the scrotum a normal appearance. If your child does not have at least one healthy testicle, your child's doctor will refer you to a hormonal specialist (endocrinologist) to discuss future hormonal treatments that would be necessary to produce puberty and physical maturity. ResultsOrchiopexy, the most common surgical procedure to correct a single descending testicle, has a success rate of almost 100 percent. Fertility for men after surgery with a single unwanted testicle is almost normal, but it falls to 65 percent in men with two unwanted testicles. Surgery may reduce the risk of testicular cancer, but it does not eliminate it. Lifestyle and Home remedies Even after remedial surgery, it is important to check the condition of the testicles to ensure that they develop normally. You can help your child by being aware of the development of your body. Check your testicles position regularly during diaper changes and baths. When your child is about to get to puberty and you're talking about what physical changes expect, he explains how he can check his testicles himself. Testicular self-examination will be an important skill for early detection of potential tumors. Copying and Support If your child does not have one or both testicles, it might be sensitive about his or her appearance. You may have anxieties about looking different from friends or classmates, especially if you have to undress in front of others in a wardrobe. The following strategies could help you cope: Preparing your appointment An unwanted testicle is usually detected at birth. Your family doctor or pediatrician will continue to monitor the condition during scheduled regular exams, or baby visits, for your younger child. To prepare for your appointment, type a list of questions to discuss with your doctor. Questions might include: Do not hesitate to ask additional questions during your appointment. What to expect from your doctor Your child's doctor will examine your child's English. If a testicle is not in the scrotum, you will try to locate it by slightly pressing against your skin. The doctor may use a lube or warm water and soap for the test. If the doctor feels the testicle somewhere in the inguinal channel, he will try to move it gently to the scrotum. If you move only partly to the scrotum, if the movement seems to cause pain or discomfort, or if the testicle immediately withdraws to its original location, it could be an unwanted testicle. If the testicle can be moved relatively easily in the scrotum and stay there for a while, it is more likely than a retractable testicle. If your child's testicle has not descended or cannot be located at the time your child approaches the age of 6 months, the doctor will refer you to a specialist in genital disorders and the urinary tract of children ( pediatric urologist) or a pediatric surgeon for further examination. RelatedAssociated Procedures Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., has been recognized as the hospital of Urology in the nation by 2020-2021 by the United States World News Report. An unwanted testicle Advert Mayo Clinic does not support companies or products. Advertising revenues support our non-profit mission. Mayo Clinic Market Take a look at these best-sellers and special offers in Mayo Clinic books and newsletters. Any use of this site constitutes your agreement with the following Terms and Conditions and the Privacy Policy. A single copy of these materials can be reprinted for non-commercial personal use only. "Mayo", "Mayo Clinic", "MayoClinic.org", "Mayo Clinic Healthy Living", and the Mayo Clinic triple shield logo are trademarks of the Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. This site complies with the information:
We use cookies and similar tools to give you the best experience on the website. By using our site, you accept our . We have a limited supply of COVID-19 vaccines and offer eligible patients based on state and federal guidelines. Please don't call us for a vaccine date. We are notifying patients individually when they can schedule. so we can notify him. More information about it. Family support When your child receives medical care, we can help make the experience easier for your entire family. Visit of your child If you are bringing your child for a visit, surgery or hospital stay, we can help you and your family prepare for the experience. About us We strive to provide your family with the most advanced medical care possible, in a family-centred environment. Surgery for unwanted testicles Many babies with unwanted testicles, also known as cryptorchidism, do not need treatment, because testicles move to the scrotum within the first months of life. But if a child's testicles have not descended for 6 to 12 months, NYU Langone's pediatric urologists recommend surgery to take them to the scrotum. Untreated and unused testicles are vulnerable to changes that can contribute to . Having an unwanted testicle is a risk factor for . OrchiopexiaIf a child's unwanted testicles are palpable, or may be felt by a doctor, a pediatric urological surgeon may perform a surgical procedure called orchiopexia to reposition them. An orchiopexia is an outpatient procedure that takes place in the hospital and requires general anesthesia. NYU Langone's pediatric urologic surgeons have experience in performing this surgery in children only 6 months. During the procedure, the surgeon makes a small incision in the English or scrotum. The surgeon releases the testicles from their surrounding attachments and places them in the scrotum. If a baby's unwanted testicles are not palpable or are high in the abdomen, a surgeon may use a laparoscope — a thin tube with a small camera at the tip — to locate the testicles. The surgeon inserts the laparoscope through a small incision in the abdomen. Then an incision is made in the scrotum. The testicle moves from the abdomen to the scrotum and is secured in position. Most children only need surgery to correct this condition. Sometimes, if the testicles are located in the abdomen, the blood vessels attached to them may not be long enough to allow the testicles to be placed in the scrotum. Two surgeries performed several months away may be necessary to position the testicles safely in the scrotum. Orchiopexia complications are rare but may include bleeding and infection. Testicular atrophy, or loss of testicles, is rare but may occur, especially when a blood vessel attached to a testicle has to be divided to gain enough length to perform the surgery. What to Expect After Surgery Most children can return home on the day of surgery. The doctor may prescribe a mild painkiller, such as acetaminophen. To promote healing and prevent discomfort, NYU Langone doctors recommend that your baby avoid toys or reward seats on the days after surgery. However, it is important that infants and children continue to chain in their safety seats to avoid injuries during the journey. NYU Langone doctors usually recommend a follow-up visit of 10 to 14 days after surgery. During this appointment, they determine whether your child feels better and healthy. The points used to close the incision are dissoluble. Another follow-up visit is usually scheduled for about four months after surgery. This allows the doctor to review your child. We can help you find a doctor at Hassenfeld's Children's Hospital. Call or . Explore NYU Langone

the-ups-and-downs-of-undescended-testes -what-pediatric-providers-need-to-know
Orchiopexy and Circumcision | Journal of Medical Insight
Orchiopexy - Wikipedia
Treatment Options for Children With Undescended Testicles - Comparative Effectiveness Review Summary Guides for Consumers - NCBI Bookshelf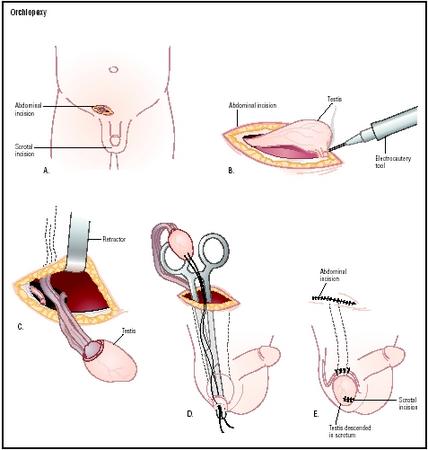
Orchiopexy - procedure, test, blood, pain, adults, time, infection, operation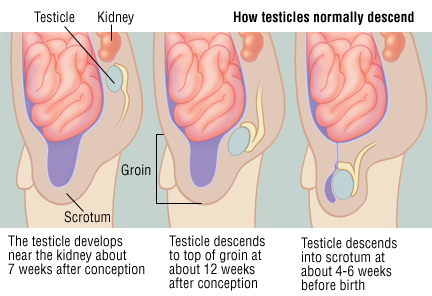
Undescended Testicle (Cryptorchidism) - Harvard Health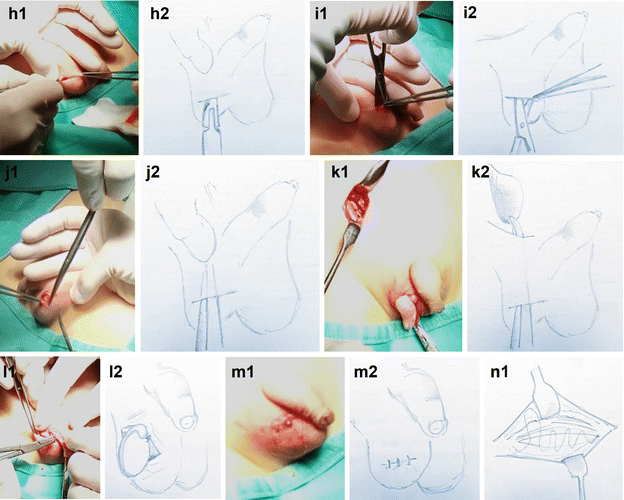
Testis Development and Descent | SpringerLink
Undescended Testicle (Orchiopexy) Repair Surgery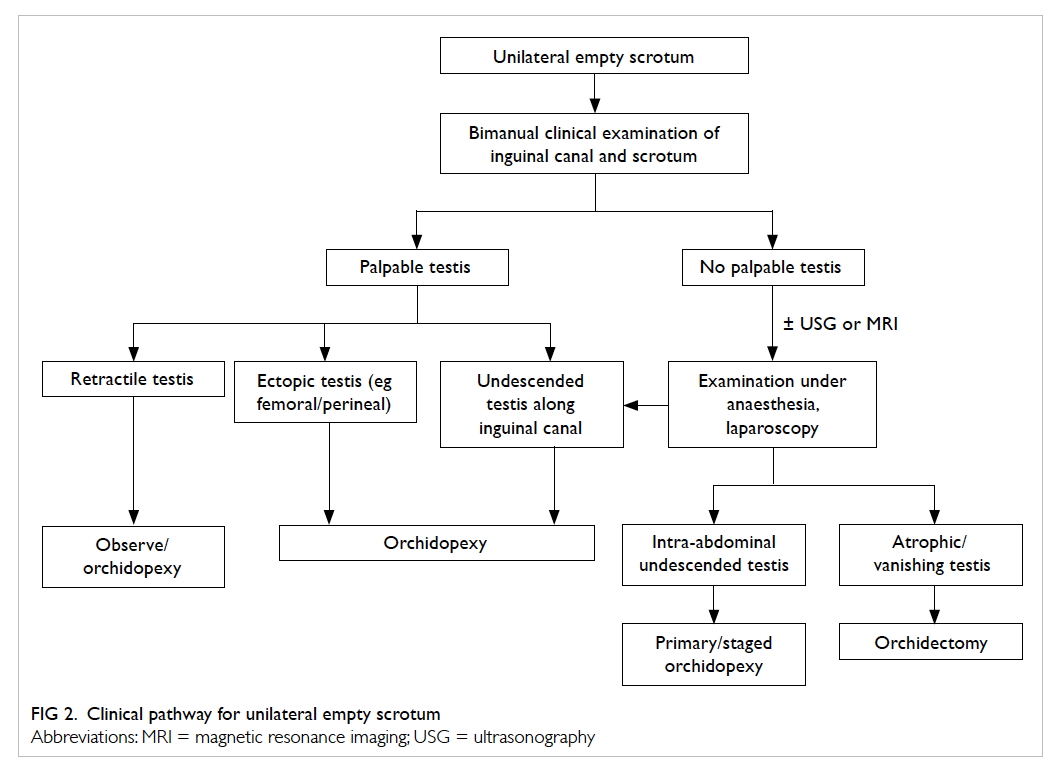
Common urological problems in children: inguinoscrotal pathologies | HKMJ
Orchiopexy
Undescended Testicle Repair: Procedure, Risks, and Complications
Undescended testes
Testicle Fixation (Orchiopexy)
Undescended Testicle Repair: Procedure, Risks, and Complications
My child was diagnosed with undescended testicles: An expert guide to what's next | Texas Children's Hospital
Cryptorchidism and Undescended Testicles - all you need to know.
Undescended Testicles: Cryptorchidism Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Undescended testes
Cryptorchidism and Undescended Testicles - all you need to know.
the-ups-and-downs-of-undescended-testes -what-pediatric-providers-need-to-know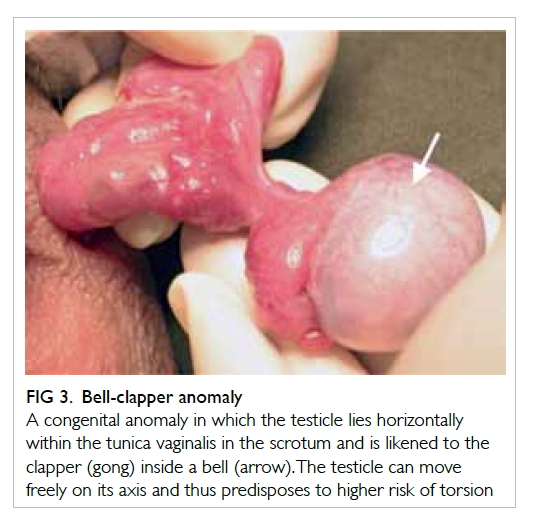
Common urological problems in children: inguinoscrotal pathologies | HKMJ
Evaluation and Treatment of Cryptorchidism: AUA Guideline | Journal of Urology
PDF) Inguinal Exploration for the Management of Impalpable Undescended Testes
PDF) Undescended testis - Current trends and guidelines: A review of the literature
Cryptorchidism and Undescended Testicles - all you need to know.
The Undescended Testicle: Diagnosis and Management - American Family Physician
PDF) Advantage of early orchiopexy for undescended testis: Analysis of testicular growth percentage ratio in patients with unilateral undescended testicle
Undescended Testicle Repair: Procedure, Risks, and Complications
undescended testicle | Medical Specialties | Sexual Anatomy
Undescended Testicle Repair: Procedure, Risks, and Complications
PDF) Management of undescended testes: a retrospective study from a tertiary hospital in Ethiopia
When the scrotum is empty: undescended testes don't only affect kids
Testis Development and Descent | SpringerLink
PDF) Inguinal Exploration for the Management of Impalpable Undescended Testes
Cryptorchidism and Undescended Testicles - all you need to know.
PDF) Management of boys with nonpalpable undescended testes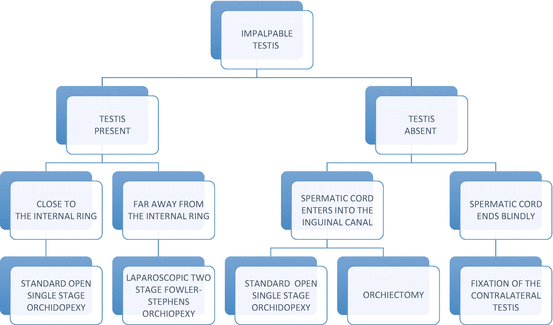
Testis Development and Descent | SpringerLink
PDF) Undescended testis and torsion: Is the risk understated?
Cryptorchidism and Undescended Testicles - all you need to know.
 Cryptorchidism: Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment - Urology Care Foundation
Cryptorchidism: Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment - Urology Care Foundation

































Posting Komentar untuk "which is a surgical procedure to reposition an undescended testicle and fix it within the scrotum?"